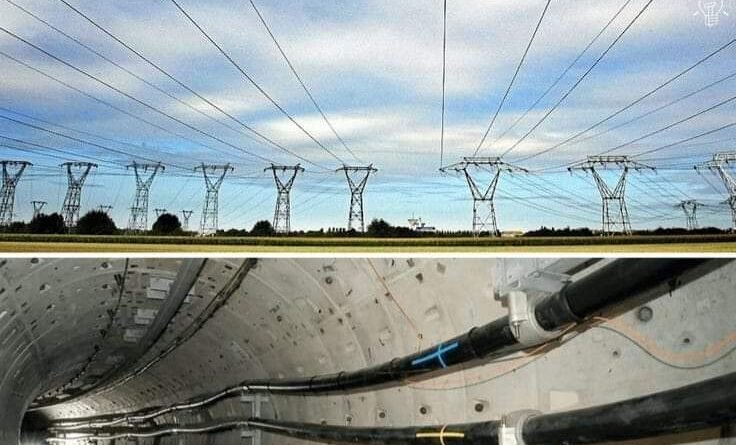
Difference between overhead and underground systems?
Difference between overhead and underground systems?

The primary differences between overhead and underground systems in terms of electrical power distribution include installation, maintenance, cost, reliability, and aesthetic impact. Here are some key points to consider:
Overhead Systems:
- Installation:
- Time and Cost: Generally quicker and less expensive to install.
- Materials: Utilizes poles (wood, concrete, or steel) and conductors (usually aluminum or copper).
- Maintenance:
- Accessibility: Easier to access for maintenance and repairs.
- Exposure: Susceptible to weather conditions, falling trees, and wildlife interference.
- Cost:
- Initial Cost: Lower initial installation cost.
- Maintenance Cost: Potentially higher maintenance costs due to frequent repairs.
- Reliability:
- Vulnerability: More prone to outages due to environmental factors (storms, high winds, ice).
- Restoration: Typically faster to repair, leading to shorter outage durations.
- Aesthetic Impact:
- Visibility: More visually intrusive as lines and poles are visible.
- Community Impact: This can affect the aesthetic appeal of neighborhoods and natural landscapes.
Underground Systems:
- Installation:
- Time and Cost: More time-consuming and expensive to install due to trenching and specialized equipment.
- Materials: Uses insulated cables, conduits, and often more durable materials to protect against underground conditions.
- Maintenance:
- Accessibility: Harder to access, requiring excavation for repairs.
- Protection: Less susceptible to weather conditions and external physical damage.
- Cost:
- Initial Cost: Significantly higher initial installation cost.
- Maintenance Cost: Generally lower maintenance costs, though repairs can be more expensive when needed.
- Reliability:
- Vulnerability: Less prone to outages from environmental factors.
- Restoration: Repairs can take longer due to the difficulty in locating and accessing faults.
- Aesthetic Impact:
- Visibility: Not visible, preserving the visual appeal of the area.
- Community Impact: Preferred in urban and high-traffic areas for minimal disruption and improved aesthetics.
Summary:
- Overhead systems are more cost-effective and easier to maintain but are more vulnerable to environmental damage and are visually intrusive.
- Underground systems offer greater reliability and aesthetic benefits but come with higher initial costs and more challenging maintenance.
Each system has its advantages and is chosen based on factors like budget, environment, aesthetic considerations, and the specific needs of the area.